May 22 2025 at 06:00PM
AI in project management: the good and the bad
AI is no longer an abstract concept addressed only to engineers, but in the recent years it has gained momentum in a variety of domains and industries, creating a technological advancement for a plethora of organizations.
When we consider the advantages of integrating AI solutions into current processes and ways of working, it is not only the increase in productivity, but also the opportunity of having a support in decision-making which could give the organizations that specific competitive advantage they are aiming for.
What are the current statistics revealing about AI adoption in companies?
Let’s take a look at the rather shocking prediction made by Gartner in 2019 referring to the Project management discipline being eliminated 80% by 2030 due to AI taking over data collection, tracking and reporting functions (Gartner, 2019).
However in a recent report run by Boston Consulting Group in 2024, despite the intense attention on AI, the companies are far from the prediction made by Gartner: only 22% of companies have developed capabilities to handle more than initial proof of concepts and actually drive value from AI implementations, while only 4% of companies report AI capabilities across multiple functions (BCG, 2024).
As for the claim that employees will be replaced by AI solutions, in a global survey from 2025 conducted on 1800 executives, the overall key take-away is that 68% of companies expect to maintain the number of employees, while efforts are being driven to provide training on AI to their employees, still an obvious need since only a third of the surveyed companies have trained a quarter of their employees in AI (BCG, 2025).
In Project management, the AI solutions are mostly used for reporting (34%), decision support (33%) and communication (26%) (PMI, 2023).
Also in the PMI annual global survey from 2023 it was revealed that only 18% of project managers were having extensive or good knowledge of AI tools, while 49% were reporting little to no experience of using AI within projects (PMI, 2023).
What AI solutions can be adopted for Project management?
Let’s take a look at different types of AI solutions, what their patterns are, how they are used and what kind of direct applications may have for projects.
AI design patterns are established approaches for solving common challenges in the creation and deployment of artificial intelligence systems. These patterns serve as best-practice templates, helping developers design algorithms and workflows that are not only scalable and maintainable but also resilient.
Similar to traditional software design patterns, AI design patterns offer structured solutions to recurring problems, but they are adapted to the unique demands of AI and machine learning (Bhat, 2025). The AI lifecycle is bound to the following concepts:
- data collection and preparation: this first step is crucial to ensure the quality of data and fit degree for the training;
- model training: this step refers to the process of realizing an efficient and effective training in line with the requirements;
- deployment: the model is deployed into real environment, being continuously monitored for high level of performance, deviations, compliance, ethical standards;
- continuous learning: the cycle would not be complete without continuous adaptation and iterative improvements according to findings from feedback loops.
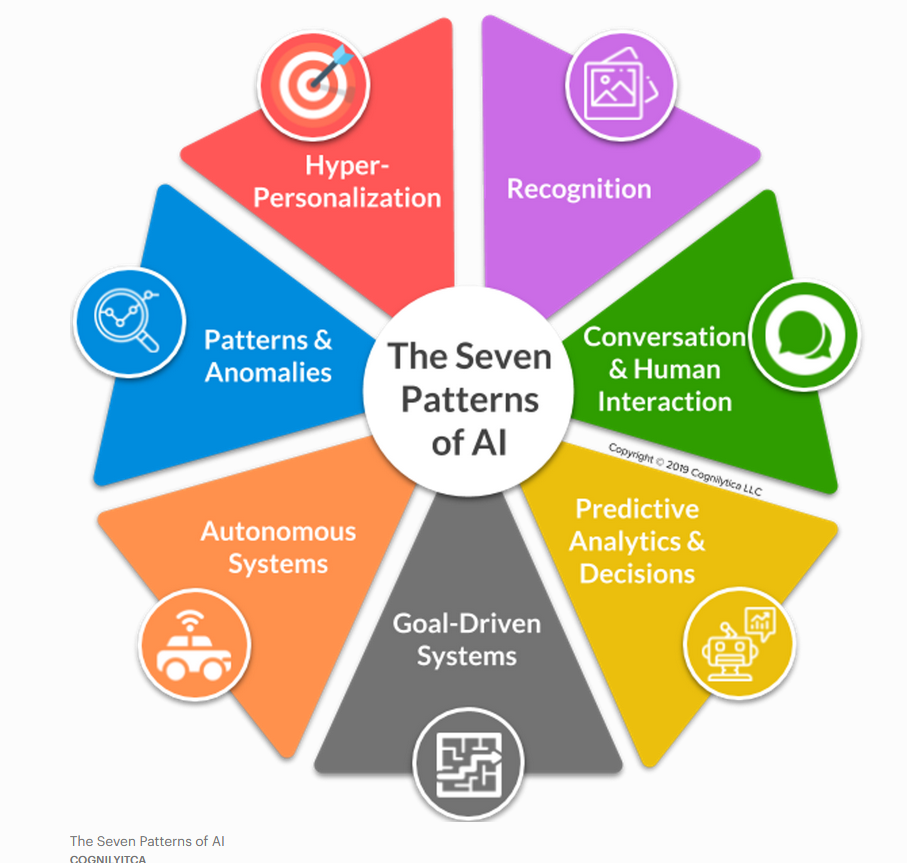
Despite the diversity of AI applications, there was achieved an agreement on how many patterns could be distinguished (Walch, 2019), as following:
- The Hyper-personalization Pattern: tailored approach to each customer
The hyper-personalization pattern leverages machine learning to create dynamic, evolving profiles for each individual, allowing systems to deliver highly tailored experiences. This approach continuously learns and adapts based on user behaviour, enabling a wide range of applications, from personalized content delivery to product recommendations. This patterns is recognizing each user as an individual and builds on those preferences, applications being built on browsing and search behaviours.
Key example for such pattern is the Netflix streaming provider and the feature to recommend shows and movies based on previous and viewing history.
One particular application of hyper-personalization pattern in project management is created by project management platforms like Asana, Trello and ClickUp which utilize AI and data analytics to personalize user experiences. These tools can adjust task presentations based on individual preferences—for instance, visual learners might receive tasks in a Kanban board format, while others might prefer list views. Additionally, communication methods can be tailored; some team members may opt for detailed emails, while others prefer concise real-time chats. This level of personalization ensures that each team member interacts with the project in the most efficient way.
- Autonomous systems Pattern: reducing the manual labour
Autonomous systems are advanced hardware and software systems capable of executing tasks, achieving goals, and interacting with their environments with minimal human intervention. Unlike hyper-personalization, which focuses on treating people as unique individuals, the core aim of autonomous systems is to minimize human involvement while maximizing efficiency and adaptability.
This design pattern relies heavily on machine learning, enabling systems to independently perceive their surroundings, predict future changes, and plan accordingly. These systems must be capable of real-time decision-making, allowing them to adapt to unpredictable situations without constant human oversight, couple of examples are: autonomous vehicles like self-driving cars, boats, trains, and drones.
In Project management, the application of autonomous systems is represented by diverse solutions to automatically schedule meetings, reassign tasks, send updates, such as the IBM Watson Orchestrate.
- AI powered predictive analytics
This approach leverages machine learning and other cognitive techniques to analyze past and present behaviours, enabling the prediction of future outcomes. Its primary goal is to provide insights to make more informed decisions, reducing uncertainty and enhancing strategic planning.
In Project management, the AI powered predictive analysis is used for risk management to analyse project data and forecast potential risks, creating risk response plans as well.
Al powered predictive analytics are used as a support in project planning: leverage Monte Carlo simulations to anticipate the impact of weather-related delays on construction timelines. This approach allows the Project manager to proactively adjust schedules and implement mitigation strategies (PMI, 2025).
- The Conversational Pattern
The conversational or human interaction pattern in AI is focusing on creating the communication between humans and machines through natural, conversational methods. This can include voice, text, and image-based interactions, allowing for machine-to-human, human-to-machine, and continuous back-and-forth exchanges. The primary goal is to make machine interactions feel as intuitive and human-like as possible.
In project management, such use of conversation pattern is provided by Asana through the AI teammates and chatbot interface which can provide answers to risk questions, summary of progress, tasks creation and assignment (Asana, 2025).
- Identifying Patterns and anomalies with AI
This pattern is used to uncover hidden relationships and detect unusual behaviour in data. It is using machine learning to identify regular patterns and higher-order connections between data points, distinguishing what aligns with established norms and what stands out as a deviation.
Some common examples are the fraud detection and risk assessment where the goal is to identify abnormal transactions or activities that deviate from expected behaviour. Another example is the predictive text, which learns from common language patterns to suggest words and phrases, helping users type faster and with fewer mistakes.
In Project management, Projectnext.ai is providing solutions for analysing large amount of data, monitoring and communication mechanisms to warn user on potential delays, lower production rates, errors on commit stage, etc. (Projectnext.ai, 2025).
- The Recognition Pattern
The recognition pattern in AI refers to the use of machine learning and cognitive techniques to identify and interpret objects, sounds, text, or other entities within unstructured data like images, audio, or handwritten notes. The primary goal of this pattern is to enable machines to accurately perceive and understand the world around them.
In project management, recognition pattern can be used in reports generated by analysing and interpreting complex visual data, such as charts, graphs, dashboards. Another use is provided by the AI solutions with speech recognition capabilities and thus transcribing project meetings or brainstorming sessions in real time.
- Goal-driven systems pattern
By applying reinforcement learning and other cognitive techniques, organizations can enable their AI systems to learn through continuous feedback, gradually optimizing their strategies for complex, real-world challenges. This pattern is particularly effective in scenarios requiring adaptive decision-making, such as resource optimization, iterative problem solving, real-time bidding, and dynamic process improvement.
Goal-drive systems pattern is used in project management to facilitate decision-making in complex project scenarios: by analysing historical data, the system can suggest action, thus helping the project manager to navigate uncertainties.
This pattern is also used for resource planning and resource capacity management, considering previous data from projects and trends in resource in utilizations, tools like Mosaic can provide support with resource allocation, capabilities gap based on the current workload and backlog, etc.
Challenges of AI adoption within project management
When considering the challenges of adopting AI solution for project managers, we can expect similarities deriving from any other organizational change since the implications of AI do not stop at the level of technology, which yes it can represent a challenge, but they can span a variety of areas, such as: the human factor (resistance to change), the ethical considerations, the data availability and resourcing, the strategical alignment and budget allocations.
While trying to increase the adoption of AI solutions, companies should pay attention at the perception of employees towards AI and any concerns should be addressed with transparency.
In a recent study conducted by McKinsey, it was found that employees are three times more likely to use AI tools than their leaders think, but they need more training and access to AI tools, and they also consider that financial rewards could stimulate the adoption rates (McKinsey, 2025).
When AI solutions started to be widely implemented, a series of ethical, fairness and copyright considerations emerged as challenges and reasons for having clear, regulated standards. In connection to the data challenge of having vetted data, AI use may also introduce bias, privacy and ethical aspects. Without proper safeguards, this data or the results provided by AI can be exposed to unauthorized access or misuse, leading to privacy violations.
The broader ethical considerations, such as transparency and accountability, may pose serious problems and create long-term consequences if Project managers rely heavily on opaque AI systems without filtering the results through a rigorous, both ethical and legal, framework adapted to organization’s context, environment and needs.
To address these challenges, organizations should prioritize building transparent, fair, and privacy-respecting AI systems. This includes implementing regular bias audits, establishing clear data governance policies, and ensuring that human oversight remains a critical component of AI solutions implemented for project management.
Despite the new investments in AI, companies still struggle with the alignment of newly strategic directions provided by AI and one of the major blocker for AI adoption is the lack of business benefits/ROI as per the study conducted by BCG. Overall the majority of initiatives which bring value are in the area of advanced analytics and enhancements for AI infrastructure, followed by risk management, considered one of top priority by 44% of respondents (BCG, 2025)
As organizations embrace AI within project management, they must balance AI’s capabilities and limitations and address the possible drawbacks with transparent and convincing solutions for their employees. This means investing in data quality, maintaining strong ethical standards, and fostering a culture of continuous learning. By focusing on the needs of organization and embedding the AI solutions within current processes and culture, Project professionals have a difficult task of supporting their leaders in crafting strategies to harness the power of new technologies, while maintaining the human touch that remains at the heart of every successful project.
References:
- Gartner (2019) Gartner Analysts to Discuss Project Management Technology Trends at the Gartner Program & Portfolio Management Summit
- BCG (2024) AI adoption 2024 https://www.bcg.com/press/24october2024-ai-adoption-in-2024-74-of-companies-struggle-to-achieve-and-scale-value
- BCG (2025) From potential to profit: closing the AI impact gap https://www.bcg.com/publications/2025/closing-the-ai-impact-gap
- PMI (2023) Shaping the future of project management with AI https://www.pmi.org/learning/thought-leadership/ai-impact/shaping-the-future-of-project-management-with-ai
- Bhat, A.K. (2025) AI design patterns: understanding RAG pattern, IEEE Computer society https://www.computer.org/publications/tech-news/trends/ai-design-patterns
- Walch, K. (2019) The seven patterns of AI, Forbes https://www.forbes.com/sites/cognitiveworld/2019/09/17/the-seven-patterns-of-ai/
- PMI (2025) Integrating Predictive Analytics into Project Management Practices
- Asana (2025) https://asana.com/product/ai/project-management
- Projectnext.ai (2025) https://projectnext.ai/blog/how-ai-detects-anomalies-to-prevent-project-delays/
- Mayer, H., Yee, L., Chui, M., Roberts, R. (2025) Superagency in the workplace: Empowering people to unlock AI’s full potential, McKinsey & Co.



